 Etiology
Etiology
- 80% of PE arise from propagation of lower limb DVT
- Other causes
- Septic emboli – from endocarditis
- Tumour
- Fat, air, amniotic fluid emboli
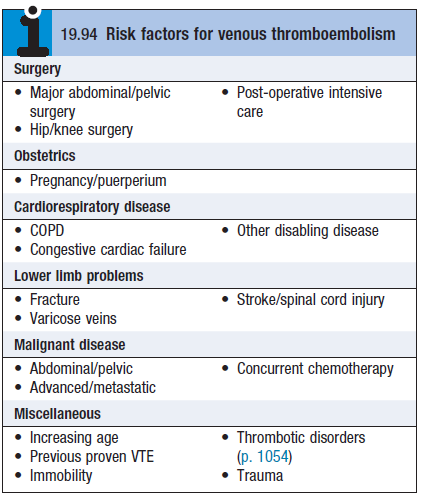
- Risk factors – see box
Pathophysiology
- DVT clot forms due to combination of sluggish blood flow, local injury/compression of vein, and hypercoagulable state
- After PE, lung tissue is ventilated but not perfused
- Leads to intrapulmonary dead space and impaired gas exchange
- The non-perfused lung no longer produces surfactant
- Alveolar collapse occurs – exacerbates hypoxemia
- Hemodynamic consequences of PE
- Reduction in cross-sectional area of the pulmonary arterial bed
- ↓in cross-sectional area of pulmonary arterial bed
- Leads to ↑PAP + ↑RV afterload → ↓CO
Clinical features + Diagnosis
- Hypotension indicates massive PE
- Clinical status at presentation is divided into ‘high risk’ and ‘not high risk’ – based on presence of shock or hypotension
- If patients are ‘not high risk’ then probability of PE is determined using Wells rule (see bottom)
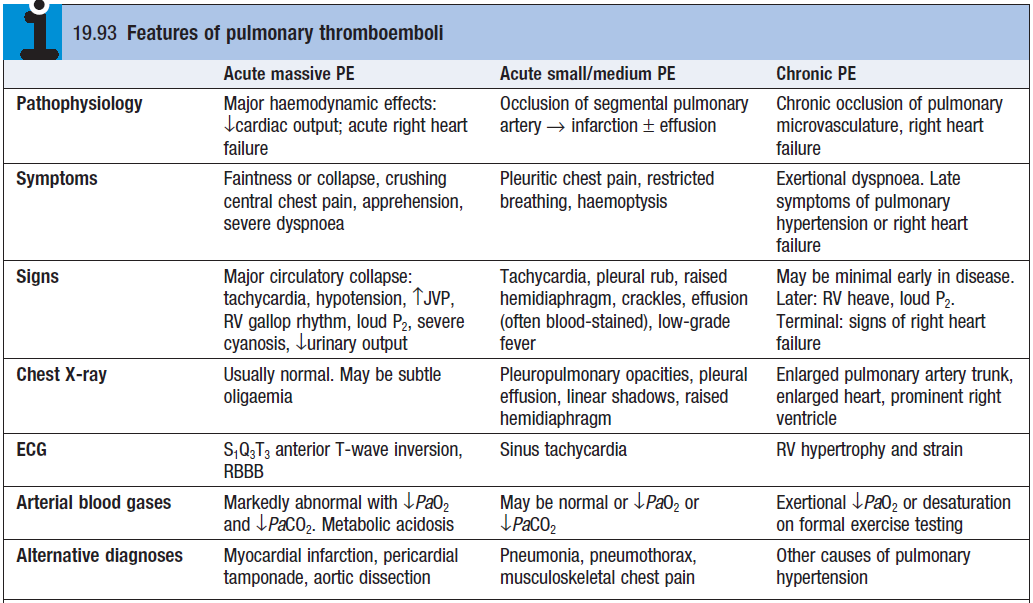
- Troponins + BNP – increased
- D-dimer – positive. Negative test excludes PE (but can also be (+) in MI, pneumonia, sepsis)
- Radionuclide V/Q scan– pulmonary 99mTc shows underperfused areas
- Ultrasound – to detect clot in pelvic/iliofemoral veins
- CT angiogram + MRI
- Echo – to assess for RV dysfunction
Treatment
Acute management
- High flow oxygen
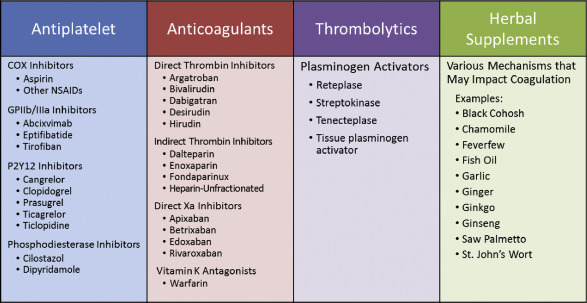
- Anticoagulants – s.c LMWH [5000UI loading dose + 18U/kg/hrs continuous] or fondaparinux [2.5mg]
- IV fluids + inotropic agents – to improve pumping of right heart
- Thrombolysis – to improve pulmonary perfusion
- Indicated in every pt presenting with acute massive PE and cardiogenic shock
- Streptokinase
- Surgical embolectomy
Prevention of further emboli
- Prophylactic anticoagulants
- Warfarin (Vit K antagonist) – for 3-6 months, INR 2-3
- Dabigatran (direct thrombin inhibitor); rivaroxaban + apixaban (Xa inhibitor) – safer than warfarin
- LMWH heparin – for pts with cancer/pregnant
- Caval filter – inserted via the femoral veins