1. ATRIOVENTRICULAR BLOCK
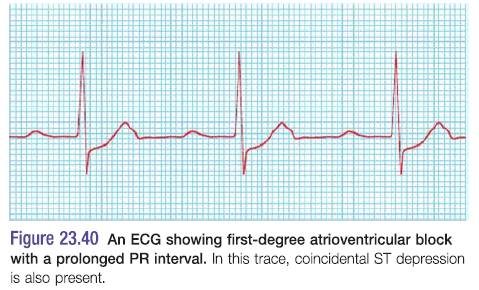
First degree AV block
- Simple prolongation of PR interval to>0.22S
- Every atrial depolarisation is followed by conduction to the ventricles but with delay
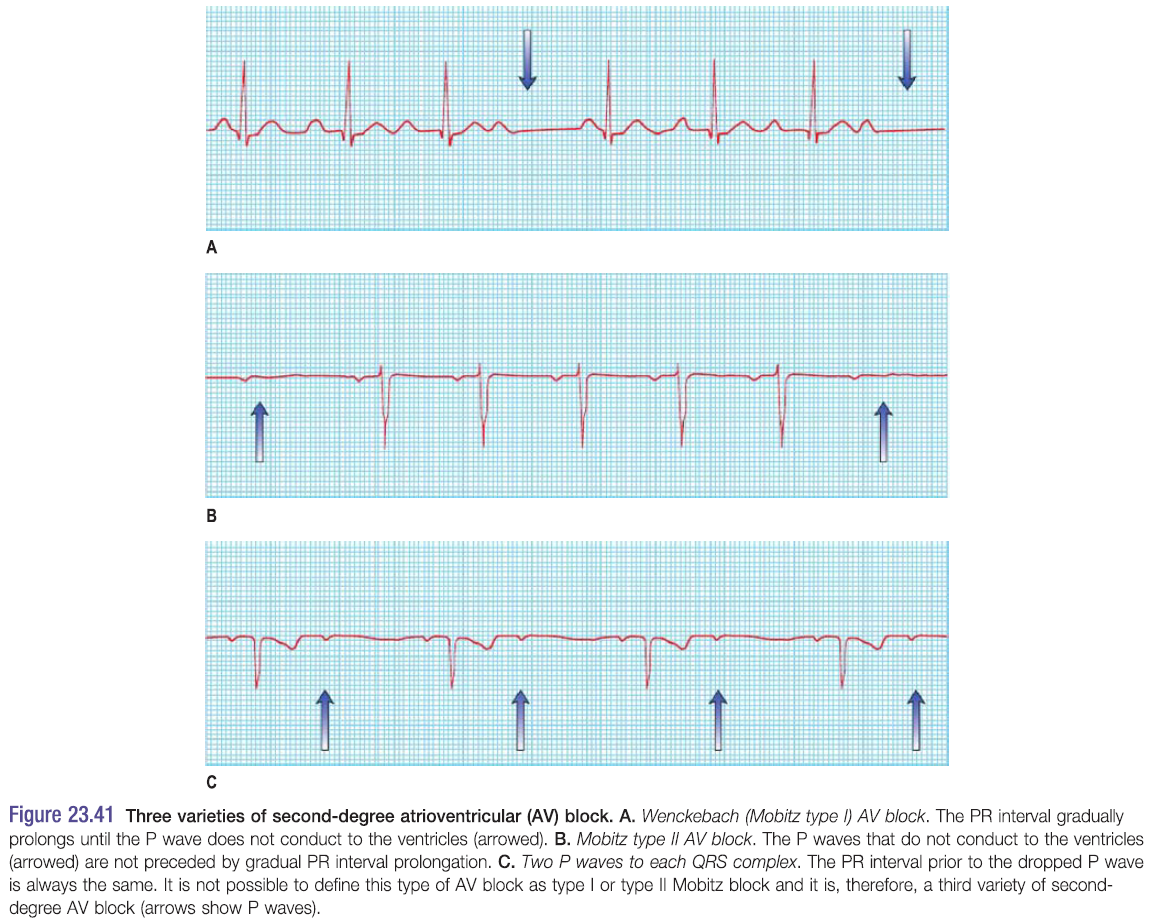
Second degree AV block – see pic
- Occurs when some P waves conduct and others don’t
Mobitz I block – due to block in AVN (atrioventricular block)
- AKA Wenckeback block
- Progressive PR interval prolongation until a P wave fails to conduct
- The PR interval before the blocked P wave is much longer than the PR interval after it
Mobitz II block – due to infranodal block e.g. in His bundle
- Occurs when a dropped QRS complex is not preceded by progressive PR interval prolongation
- QRS is normally wide >0.12s
2:1 or 3:1 block
- Occurs when every 2nd or 3rd P wave conducts to the ventricles
Management
- Mobitz I – usually only requires monitoring
- Mobitz II – higher risk of progression to complete heart block
- Pacemaker indicated
Third degree (complete) AV block
- Occurs when all atrial activity fails to conduct to the ventricles
- Spontaneous escape rhythms maintain life
- Etiology –
Narrow complex escape rhythm – QRS <0.12s
- Imply that it originates in His bundle – so region of block is in AVN
- Escape rhythm is 50-60bpm – reliable
- IV atropine – for recent onset narrow complex AV block (NCAVB)
- Permanent pacing – for chronic NCAVB
Broad complex escape rhythm – QRS >0.12s
- Implies that escape rhythm originates below His bundle
- So block lies in His-Purkinje system
- Escape rhythm is slow (15-40bpm) – unreliable
- CF – Stokes-Adams attacks (dizziness + blackouts)
- Permanent pacing
- ICD
2. BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK (BBB) 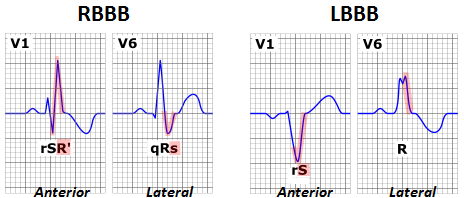
- His bundle gives rise to right and left bundle branches
- Left bundle subdivides into anterior and posterior divisions
Etiology
- RBBB – isolated congenital anomaly; cardiac/pulmonary diseases
- A/VSDs, tetralogy of Fallot
- Pulm stenosis, PE, PHTN, MI
- Complete LBBB – extensive LV disease
Bundle branch conduction delay
- Produces slight widening of QRS complex – incomplete BBB
Complete BBB
- Associated with a wider QRS >0.12s
- Shape of QRS depends on whether the right or left bundle is blocked
Right BBB– best seen in V1 (rSR)
- Produces late activation of the RV
- I + V6 – broad S wave
- V1 – tall late R wave, seen as rSR
- Second R wave here is due to the late depolarisation of the RV compared to the LV
Left BBB – best seen in V6 (M shape due to broad QRS with notched top)
- I + V6 – tall late R wave
- V1 – broad S wave
- In LBBB septum becomes depolarised from right to left – causes abnormal Q wave in V1 and R wave in V6
Hemiblock
- Delay/block in the divisions of the LBB
- Produces a swing in the direction of depolarisation (the axis)
- Left anterior hemiblock
- means the LV is activated from inferior to superior
- produces LAD (left axis deviation)
- Left posterior hemiblock
- Produces RAD (right axis deviation)
Bifasciular block
- Combination of a block of any 2 of the following
- RBB, Left anterior division, Left posterior division
