Etiology and pathogenesis
- Paraproctitis – purulent inflammation of the tissues surrounding the rectum (cellulitis)
- The most common cause is penetration of bacterial flora from the rectum to the surrounding tissue
- E.coli, anaerobes, staphylococcus, streptococcus, enterococcus
- Usually arises from the cryptoglandular epithelium lining the anal canal – leads to damage of the rectal mucosa
- Infection of the glandular secretions leads to suppurative spread – can form an abscess/fistula
- Can result as a complication of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis
Classification
Etiological
- Non specific paraproctitis
- Specific paraproctitis
- Bacillary dysentery
- Gonococcal
- Tuberculous
- Post-traumatic paraproctitis
Activity of inflammatory process
- Acute
- Recurrent
- Chronic fistulous paraproctitis
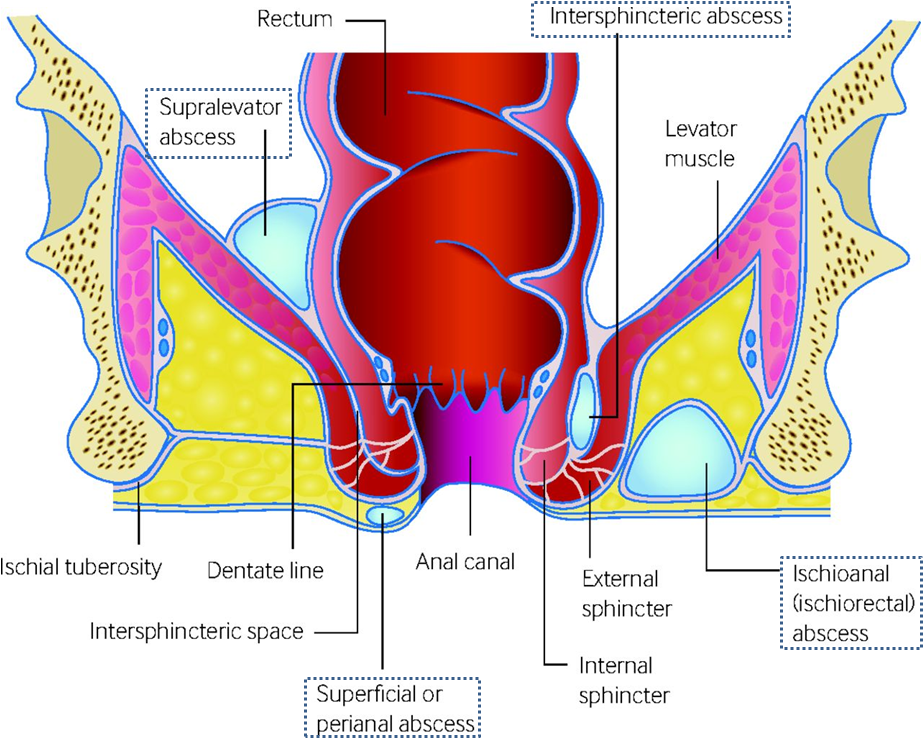
Localisation of abscess (see pic)
- Perianal – superficial collection of purulent material under skin of anal canal
- Ischio-rectal – suppuration traverses the external anal sphincter into ischiorectal space
- Intersphincteric – suppuration continues between internal and external anal sphincter
- Supralevator – upward extension from intersphincteric abscess above levator ani
- Submucosal – abscess is under the mucosa, paain and skin changes are less pronounced
Clinical features
- Initial presentation – short period of malaise, weakness, headache, fever, chills
- Severe pain in perianal region – make it difficult to sit
- Tender, smooth, soft swelling in the region
- External signs – erythema, induration
- Tenesmus, passage of mucus and blood
Investigations
- Laboratory diagnosis – blood glucose level, urine
- Stool study and culture
- US – anal and perineal
- Fistulography with contrast medium
- Proctosigmoidoscopy
Treatment
- Sitz bath, antibiotics, analgesics, local anaesthetics, laxatives
- Incision and drainage under general anaesthesia
Prevention
- Treat constipation – stool softeners, high fibre diet
- Maintain blood glucose level
Complication
- Bacteraemia and sepsis
- Seeding of infection to other areas by haematogenous spread
- Purulent fistulas between rectum and vagina
- Peritonitis
- Retroperitoneal phlegmon
