- ACS – Unstable angina , STEMI, NSTEMI
- UA – new-onset, rapidly worsening angina (crescendo angina), or angina at minimal exertion/rest in absence of myocardial damage
- MI – angina at rest and evidence of myocardial necrosis (demonstrated by ↑troponins or CK-MB)
- Difference between UA and NSTEMI
- UA – ischemia, without infarction. No obvious ECG change
- NSTEMI – occluding thrombus leads to myocardial necrosis and ↑in troponins/CK-MB
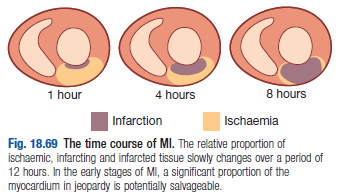
 MI occurs when cardiac myocytes die due myocardial ischemia
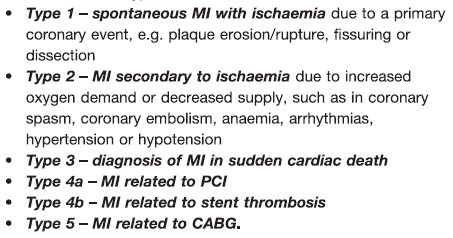
MI occurs when cardiac myocytes die due myocardial ischemia- Types of MI
Etiology
- Atherosclerotic plaque ruption/erosion
- Age, male gender
- Family history of IHD
- Smoking
- HTN
- Hyperlipidemia
- Obesity, sedentary lifestyle
Pathophysiology
- Rupture or erosion of the fibrous cap of a coronary artery plaque
- Leads to platelet aggregation + adhesion, localised thrombosis, vasoconstriction and distal thrombus embolisation
- Platelets release serotonin and TXA2 – results in thrombus formation and vasoconstriction
- Causes myocardial ischemia due to reduction of coronary BF
- Rich lipid pool within plaque and a thin fibrous cap – ↑risk of rupture