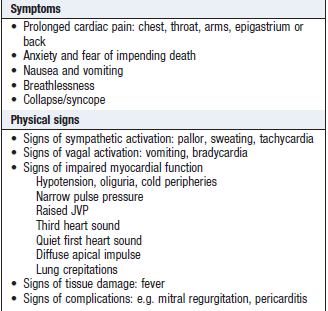
Clinical features
Diagnosis
ECG changes
- ST depression and T-wave inversion – highly suggestive of NSTE-ACS
- STEMI – complete occlusion of a coronary vessel
- Results in persistent ST-elevation
- Or LBBB
REMEMBER
- ST Elevation – infarction (irreversible damage)
- ST Depression – ischemia (reversible with prompt tx)
Biochemical markers
- Cardiac troponin complex
- Troponin levels rise from 2-24hrs after pain, peak at 24-48hrs, and return to baseline after 5-14 days
- Troponins I, T, C
- T – attaches the complex to tropomyosin
- C – binds Ca during excitation-contraction
- I – inhibits the myosin binding site on actin
- Normal serum troponin – <5ng/L
- ↑ Serum troponin – increased mortality in ACS patients
- CK-MB – raised after muscle trauma
- Levels drop back to normal after 36-72hrs
- Replaced by troponin testing, but can be used to determine re-infarction
Differential diagnosis
Cardiac
Pulmonary
Oesophageal
- Reflux or spasm
- Tumour
- Oesophagitis
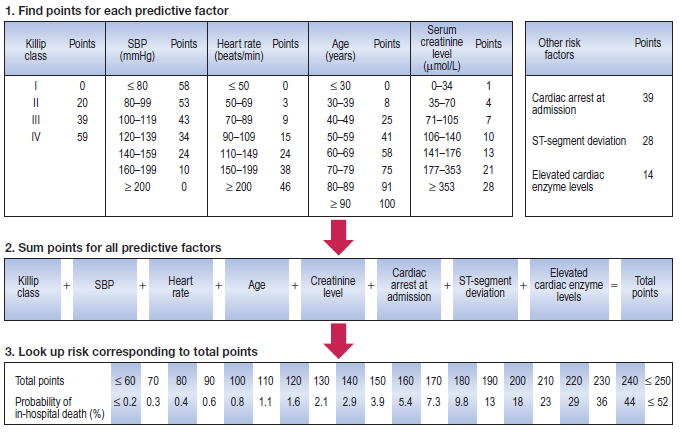
Risk stratification – Grace Score
- Risk stratification is important because it guides the use of pharmacological and interventional treatment
![]()

