- Characterised by diffuse hepatic fibrosis and regenerative nodule formation
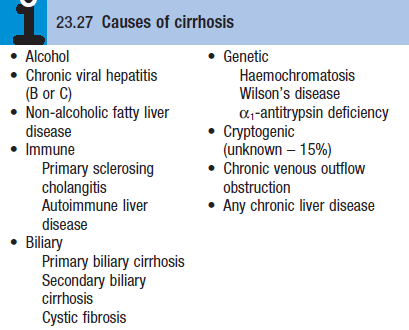
Etiology
Pathophysiology
- After liver injury stellate cells in space of Disse are activated by cytokines produced by Kupffer cells + hepatocytes
- TGF-β, PDGF
- Transforms the stellate cells into a myofibroblast-like cell, capable of producing collagen, pro-inflam cytokines and other mediators – promotes hepatocyte damage and tissue fibrosis
- Cirrhosis is a histological diagnosis – progressive fibrosis and wide spread hepatocyte loss
- Lead to distortion of the liver architecture → disrupts hepatic vasculature, causes Portosystemic shunts
- Histological classification
- Micronodular – small nodules (1mm), typically seen in alcoholic pts
 Macronodular – larger nodules of various sizes, areas of previous collapse of the liver architecture are seen a large fibrous scars
Macronodular – larger nodules of various sizes, areas of previous collapse of the liver architecture are seen a large fibrous scars
Clinical features (variable)
- Asymptomatic, diagnosis made incidentally at USS or surgery
- Nonspecific symptoms – weakness, N+V, upper abd discomfort
- Dyspnoea – due to a large right pleural effusion
- Hepatomegaly – MC in cirrhosis due to ALD or haemochromatosis
- Progressive hepatocyte destruction and fibrosis lead to decreased liver size
- Especially if cause is viral hep or autoimmune liver disease
- Mild jaundice at first, leukonychia, dupuytren contracture
- Palmar erythema – non specific
- Spider telangiectasia – above nipples (strong indicator of liver disease)
- Endocrine changes (MC in men) – los of hair, testicular atrophy
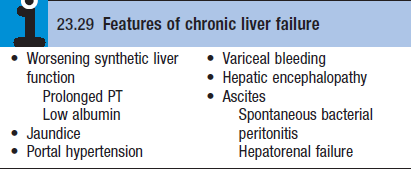
- Splenomegaly + collateral vessel formation – features of portal HTN
- Ascites – advanced
- Hepatic encephalopathy
- Non specific – clubbing of fingers and toes
- Decompensating signs
- Oedema, ascites, dilated veins, CNS
Management
- Tx underlying cause
- Colestyramine [4g/12hrs] – pruitis
- Spironolactone [100mg] – counter RAA axis
- Maintain nutrition
- Tx complications – ascites, hepatic enceph, portal HTN, varices
- Endoscopy – to screen for oesophageal varices
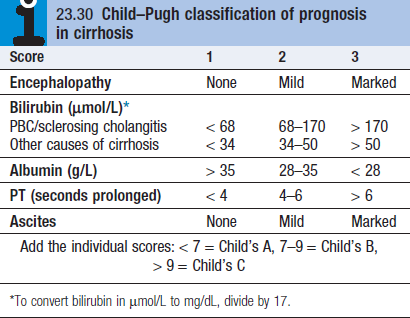
- Regular surveillance for HCC (Child Pugh Score)
- Liver transplant
