- Neuropsychiatric syndrome caused by liver disease
- Confusion is followed by coma as disease progresses
Etiology
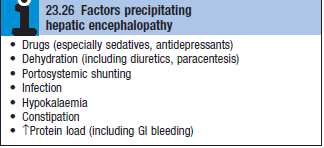
- Precipitating factors (see box)
Pathophysiology
- Disturbance of brain function provoked by circulating neurotoxins that are normally metabolised by the liver
- Most pts have evidence of liver failure and portosystemic shunting of blood
- Neurotoxins causing encephalopathy are unknown
- Thought to be nitrogenous substances produced in the gut by bacteria
- Normally metabolised by the healthy liver and excluded from the systemic circulation
- Potential compounds
- Ammonia
- GABA
- The brain in cirrhosis can also be sensitised to other factors (drugs etc) – that can precipitate condition
- Disruption of blood brain barrier is a feature of acute hepatic failure – can lead to Cerebral oedema
Clinical features
- Changes of intellect, personality, emotions and consciousness ± neurological signs
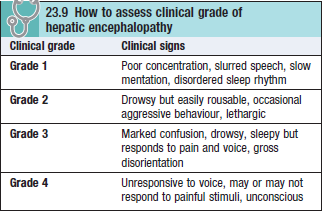
- Degree of encephalopathy can be added from 1-4
- Early features are mild
- Apathy, inability to concentrate, confusion, disorientation, drowsiness, slurring of speech, eventually coma
 Convulsions
Convulsions- Flapping tremor (asterixis)
- Inability to perform simple mental maths or draw objects
- As condition progresses – hyperreflexia
- Fetor hepaticus – sweet musty odour on breath
- More a sign of liver failure and portosystemic shunting
- Chronic HE can cause cerebellar dysfunction
- Parkinsonian syndromes, spastic paraplegia and dementia
Investigations
- Diagnosis made clinically, EEG when in doubt
- Shows diffuse slowing of the normal alpha waves, with eventual development of delta waves
- Increased arterial ammonia
Management
- Treat/remove precipitating causes
- Suppress production of neurotoxins by bacteria in the bowel (regular enema)
- Lactulose – 15-30ml tid
- Reduces pH of colonic content, so limits colonic ammonia absorption and promotes incorporation of nitrogen into bacteria
- Rifaximin – 400mg tid
- Well tolerated AB, reduces bacterial content of bowel
- Chronic/refractory HE – one of the main indications for liver transplantation
