1. HAEMOCHROMATOSIS
- Amount of total body iron is increased (normal = 4g)
- Excess iron deposits cause damage to several organs, commonly liver
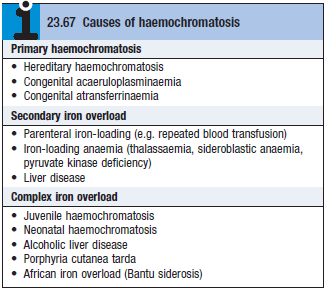
- Causes – see box
Hereditary Haemochromatosis (HHC)
- Iron deposited throughout the body ≈20-40g (N=4g)
- Organs involved – liver, pancreas islets, endocrine glands, heart
- In the liver – gradual development of fibrous septa causes formation of irregular nodules
- Regeneration results in macronodular cirrhosis
Pathophysiology
- Increased absorption of dietary Fe
- AR inheritance. Single point mutation, results in cysteine → tyrosine substitution at point 282 in HFE protein
- HFE normally interacts with the transferrin receptor in the membrane of intestinal epithelial cells
- When transferrin is ↑ (in IDA), HFE increases the intestinal release of Fe into the blood
- In HHC, mutation of HFE causes the intestines to interpret a strong transferrin signal (state of iron deficiency)
- Leads to excessive iron absorption
- Hepcidin is normally increased iron overload – internalises ferroportin 1 and Fe is trapped inside mucosal cell
- But HFE mutation also disrupts hepcidin expression – results in ↓hepcidin and facilitates iron overload
- Excess Fe is then gradually taken up by the liver and other tissues
Clinical features
- MC in men >40
- Early symptoms – fatigue, arthropathy
- Classic triad – bronze skin (melanin deposition), hepatomegaly, DM
- Impotence, loss of libido, testicular atrophy, arthritis
- Deposits in heart – cardiac failure or dysrhythmias
Investigations
- ↑serum iron, ↓TIBC
- Transferrin saturation >45% suggestive of iron overload
- ↑↑ferritin – ddx is inflammatory disease/excess ethanol consumption
- MRI
- Liver biopsy
- Hepatic Iron Index (HHI) = μmol of iron per g dry weight of liver / age in years
- HHI > 1.9 suggestive of HHC
- Gene testing – identifies mutations C282Y + H63D
Management
- Weekly venesection of 500ml blood (250mg iron) until serum iron is normal – can take 2y or more
- Aim to reduce ferritin to <50μg/l
- Liver and cardiac problems improve after iron removal, but joint pain is less predictable
- DM doesn’t resolve after venesection – may need insulin
- Investigate first degree family members
Secondary haemochromatosis
- Causes
- Many conditions requiring multiple blood transfusions – chronic haemolytic disorders, siderolastic anemia
- Dietary iron overload
- Features are similar to HHC
