 MM is characterised by a triad of abnormalities
MM is characterised by a triad of abnormalities-
- Accumulation of plasma cells in the BM
- Bone lesions – discrete or diffuse (see below)
- Production of a Monoclonal Ig
Epidemiology
- 2nd MC lymphoid malignancy in Caucasians after CLL
- MC in older people and men
- Increased incidence in people in petroleum, leather and asbestos industries
Clinical features
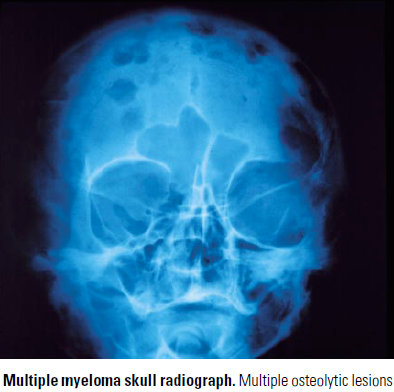
Bone lesions – caused by accumulation of plasma cells in the BM, with dissolution of the bone
- Bone pain and pathologic fractures – MC presenting complaints
- Sharp ‘punched out’ Osteolytic lesions – MC in vertebra, ribs, skull, pelvis, femur
- Less common – diffuse osteoporosis without discrete osteolytic lesions
- Bone is eroded due to increased osteoclast activity
- Osteoclasts are stimulated by factors produced by plasma cells – OAFs (osteoclast activating factors)
Infections – MCC of death in MM pts
- Normal Ig production is suppressed – pts susceptible to S.pneumoniae, S.aureus, E.coli
- Pneumonitis and Pyelonephritis are common infections
Renal disease – 2nd MCC of death
- Myeloma cast nephropathy
- Large tubular casts in urine sediment (light chain + Tamm-Horsfall (THP))
- The abnormal proteins (Ig) bind with THP >> form large tubular casts which are too big to pass >> blockage >> kidney disease
- Malignant prolif of plasma cells in BM with prod of Ig
- Ig light chains (AKA abnormal paraproteins) >> BJ proteins >> toxic to tubular system
- Light chains are filtered at glomeruli and appear as BJ proteins
- Hypercalcemia – causes inability to concentrate urine (polyuria)
- Predisposes to dehydration and prerenal azotemia
- Nephrotic syndrome – due to proteinuria
- Renal amyloidosis – due to Ig fragments precipitating as a β-pleated sheet
Hypercalcemia
- Due to excess bone resorption
- Can lead to weakness, confusion, lethargy, loss of renal concentrating ability
Diagnosis
- Dx depends on presence of 3 features
- A monoclonal Ig protein in serum/urine – electrophoresis (IgG kappa is MC)
 Bone lesions – CTI/MRI
Bone lesions – CTI/MRI- Plasmacytosis in BM – >10% plasma cells on BM aspirate
- Anemia is often the presenting feature in MM
- Hypergammaglobulinemia
- Hypercalcemia, azotemia
- ALP levels normal as no activation of osteoblasts
- M spike
- FISH – chromosome abnormalities
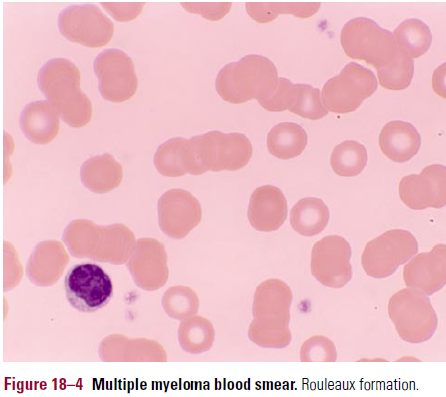
- Blood smear
- Shows stacked lines of erythrocytes – rouleaux (see pic)
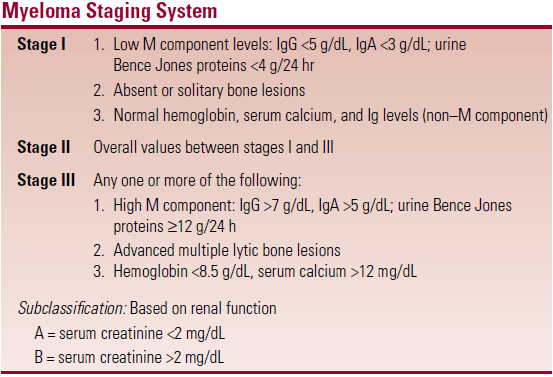
Staging – see table. Tumour burden
Complications
- Spinal cord compression
- Amyloidosis – AL (light chain)
- Hyperviscosity syndrome
 Treatment
Treatment
- Standard chemo – melphalan + prednisone
- Combo chemo – VDD
- Vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone
- Eventually disease becomes resistant to chemo
- Saline infusion and diuresis for hypercalcemia
