- Definition – a new episode of pneumonia occurring at least 2 days after hospital admission
- Health-care associated pneumonia (HCAP) – development of pneumonia in a person who has spent at least 2 days in hospital within the last 90 days, or has attended a dialysis unit, received IV antibiotics, or has been a resident in a nursing home
Epidemiology/etiology
- MCC of HAI -associated death
- High risk groups – elderly; pts on mechanical ventilation
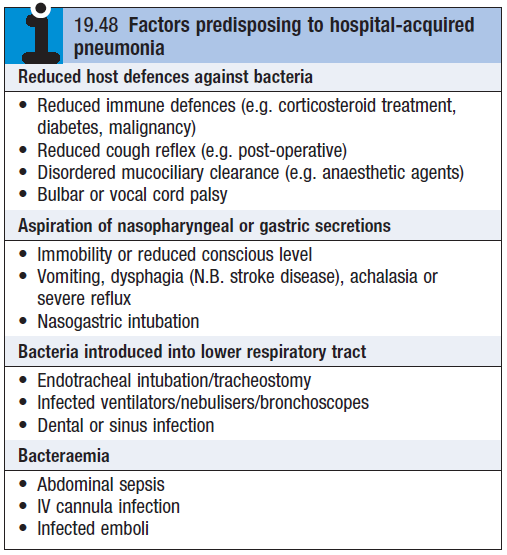
- Factors predisposing to HAP – see box
Pathogens
- Early onset HAP (within 4-5 days of hospital admission)
- Similar to CAP
- Late onset HAP (G- more common)
- E.coli, Pseudomonas, Klebsiella,
- S.aureus + MRSA
Clinical features
- Suspect HAP in any hospitalised/ventilated pt who develops purulent sputum/new radiological infiltrates/fever/leucocytosis
- Ddx – VTE , ARDS, PE
Investigations
- Microbiological confirmation
- FBC, U+E, ESR, CRP
- ABG
- CXR
- In ventilated patients – bronchoscopy-directed brush specimens; BAL ; endotracheal aspirates
Management
- Similar to CAP – oxygen, IV fluids, ABs
- Early onset HAP
- Co-amoxiclav – for pts who haven’t received a recent course of ABs
- Pipercillin/tazobactam – for pts who have had a recent course of ABs
- Late onset HAP
- ABs must cover G- bacteria, S.aureus, MRSA and anaerobes
- Carbapenem for Pseudomonas
- Vancomycin [1g/day] for MRSA
