Acute Coronary Syndrome without ST elevation
1. NSTEMI
Other conditions that cause elevated troponin
- PE
- Myocarditis
- Pericarditis
- Arrhythmias
- Renal failure
- Partial occlusion of a major coronary vessel
- Usually dx on the basis of
- A suggestive history
- ↑troponin levels (see box for ddx)
- ECG changes
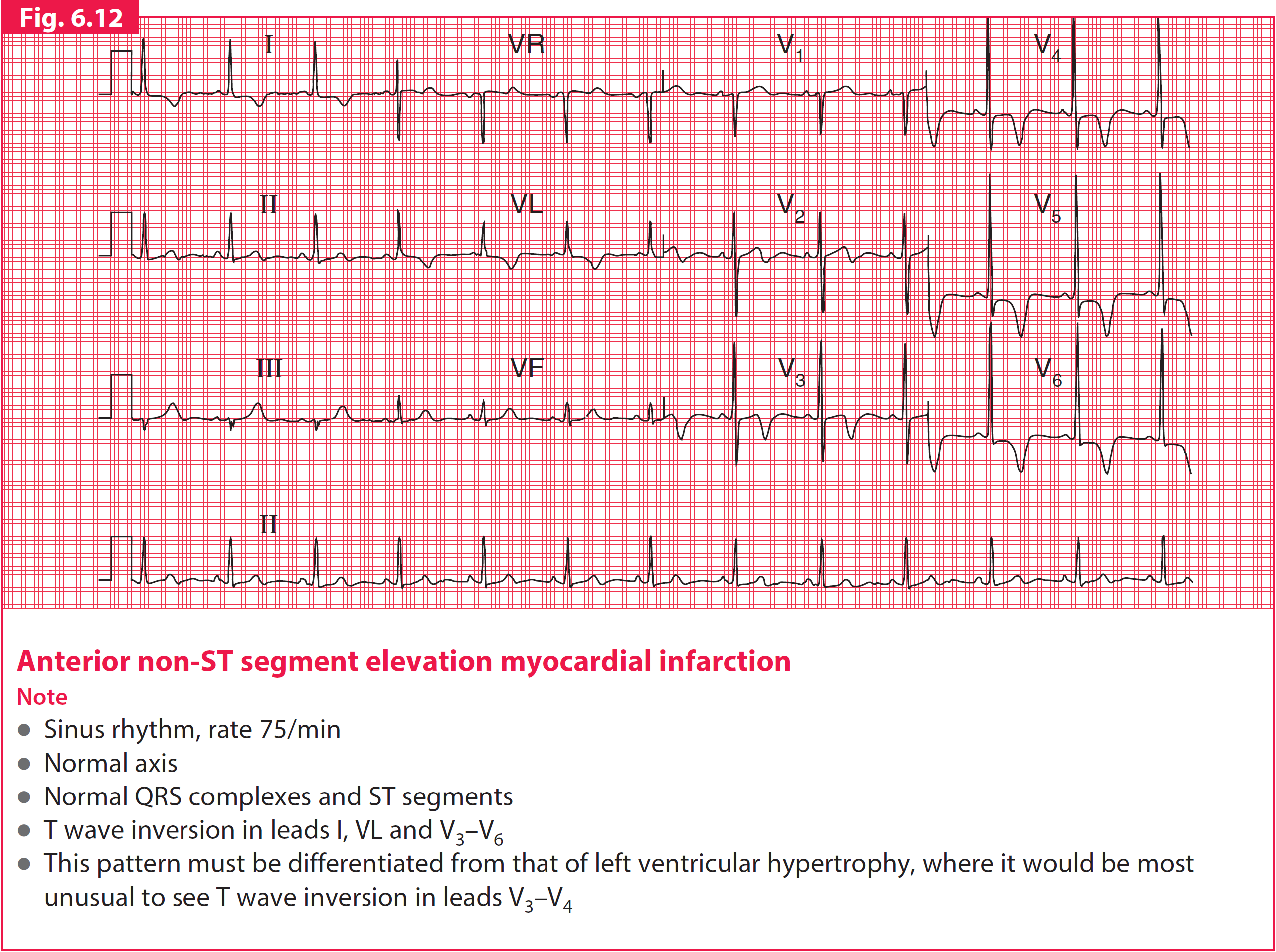
ECG changes
- No ST elevation
- No Q waves
- ECG can be normal
- Other changes can be
- ST depression
- Hyperacute T wave (tall pointy T waves) – normally resolve by the time pt is seen in the hospital
- T wave inversion – late sign. Indicates previous MI
Troponin testing
- Can be ‘traditional’ or ‘high sensitivity’ troponin test
- Traditional test
- Positive or negative test
- Serial tests performed over 6-8 hours
- Any detected troponin results in a (+) test – therefore a dx of NSTEMI
- High sensitivity test
- Based on the fact that 50% of the population has an undetectable level of troponin, 50% have a detectable level of troponin
- APPROX normal range is <5ng/L – varies from hospital to hospital
- This method does two troponin tests, 2 hours apart, within 3 hours of onset of chest pain
- A (+) test is defined as an increase in troponin between the two tests
2. UNSTABLE ANGINA
- Only distinguishable from NSTEMI through troponin testing
- TIMI Score is used to determine the likelihood of ischemic events or mortality in patients with unstable angina or non–ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) – >5 points denotes high risk.
3. TREATMENT – see topic 10-4