- Deposition of amyloid (irregular misfolded protein) in a variety of tissue → system/organ dysfunction
- Amyloid protein consists of β pleated sheets which are insoluble and resistant to proteolysis
- Amyloid material can be deposited in renal glomeruli , tubules and blood vessels
- Serum amyloid plasma protein prevents degradation and interacts w/ heparin sulphate on glomerulus
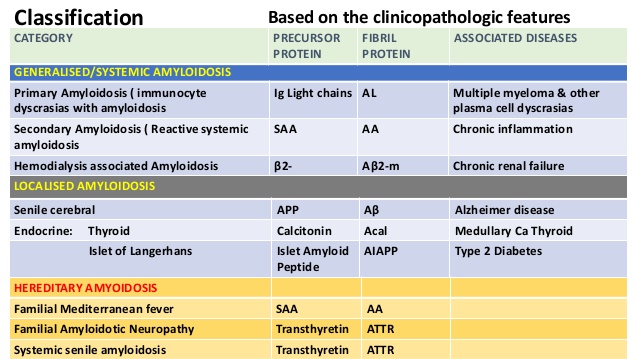
Classification based on precursor protein – see box
- Ig light chain – (AL) – primary e.g. MM
- Serum amyloid – (AA) – secondary to inflam e.g. RA, IBD, TB, FMF
- Familial/hereditary – (ATTR) – AD, due to mutant transthyretin; leads to FAN, cardiomyopathy and nephropathy
- B2 microglobulin – (AB2M) – dialysis reaction (mostly affects joints)
Renal manifestations of amyloidosis
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Nephrogenic DI
- Renal tubular acidosis
- Retro-peritoneal fibrosis
Clinical features – 4 stages
- Pre clinical – asymptomatic, dx by biopsy to see amyloid deposits
- Proteinuria – 2-20g/24h
- Nephrotic – hypoalbuminemia + hypoproteinemia
- Uremic – HTN, gylcosuria, tubular acidosis
- AL – 50% renal involvement (tx=bortezomib)
- AA – 100% renal involvement (tx=infliximab)
- Cardiomyopathy, HSM, skin, joint, adrenal, thyroid
Diagnosis
- Tissue biopsy – stain congo red
- IF – monoclonal stains of amyloid protein
Treatment
- Treatment of nephrotic syndrome – CTST, diuretics
- Renal tubular acidosis – sodium bicarbonate
- Dialysis, transplant
- Cyclophosphamide if precursor is AL (Ig)