Clinical features
General
- Headache, fatigue
- Vision problems
- Chest pain, irregular heartbeat
- Difficulty breathing
Target organ damage
- Blood vessels
- In larger arteries – thickened lamina, smooth muscle hypertrophy, deposition of fibrous tissue
- Walls become less compliant
- In smaller arteries – hyaline arteriosclerosis, lumen narrows, ↑risk of aneurysms
- Activation of RAAS due to decreased renal blood flow
- HTN is a major risk for aortic aneurysm and dissection
- In larger arteries – thickened lamina, smooth muscle hypertrophy, deposition of fibrous tissue
- CNS
- Stroke, Transient ischaemic attack , subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH)
- Papilloedema – due to ↑intracranial pressure
- Retina
Cotton wool exudates– due to retinal infarction
- Heart
- ↑incidence of coronary artery disease
- HTN causes a pressure load on the heart – causing LV hypertrophy + 4th heart sound
- Atrial fib – due to diastolic dysfunction caused by LVH or CAD
- Kidneys
- Damage to renal vasculature – Hypertensive renal disease
- High intraglomerular pressure – impairs filtration
- Results in increased protein filtration – proteinuria
- Nephrosclerosis – leading to glomerular ischemia and hyaline deposits
- Progresses to renal failure
Malignant hypertension
- BP >180/120 with end organ damage
- Characterised by accelerated microvascular damage with necrosis of walls of small arteries and arterioles
- Intravascular thrombosis
- Diagnosed by – High BP, retinopathy, renal dysfunction
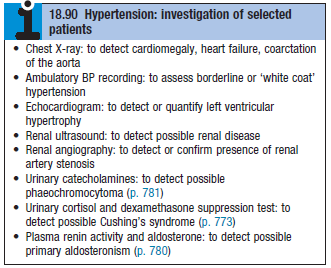 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
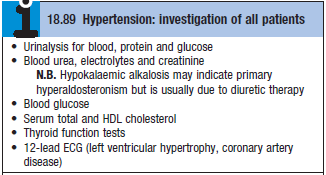
Differential diagnosis
- Amphetamine toxicity
- Anxiety disorders, apnoea
- Heart failure, myocardial infarction
- Hyperparathyroidism
- 1o aldosteronism
- Gestational HTN
