- Disease of immune-mediated liver injury – presence of serum Abs and peripheral blood T lymphocytes reactive with self-proteins
- Strong assoc with other autoimmune diseases and high levels of serum Igs (esp ^IgG)
 Commonly in young women
Commonly in young women
Etiology
- Low immune tolerance due to cross reactivity with HAV, EBV etc
- Immunologically susceptible pts – those with HLA- DR3+ DR4
Pathophysiology
Type 1 AIH – ANA + Anti-smooth muscle Abs
- Typically associated with IgG hyperglobulinemia (97% pts)
- MC in young adult females
Type 2 AIH – Anti-LKM Abs
- Anti-LKM Abs recognise cytochrome P450-IID6 expressed on hepatocyte membrane
- MC in paediatric population
- More resistant to treatment than ANA (T1 AIH)
- Adult onset of anti-LKM seen in chronic HCV inf
Type 3 AIH – Anti-soluble liver Ag
- Adult pt
- Aggressive disease, lacks autoAbs of other specificity
Clinical features
- Insidious onset, fatigue, anorexia, jaundice
- 25% pts have acute onset – resembles viral hep, but without resolution
- Leads to extensive liver necrosis and failure
- Fever, arthralgia, vitiligo, epistaxis, amenorrhoea
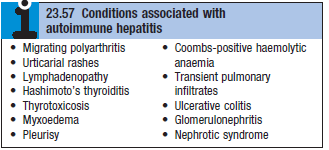
- Associated autoimmune disease – Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis etc
Investigations
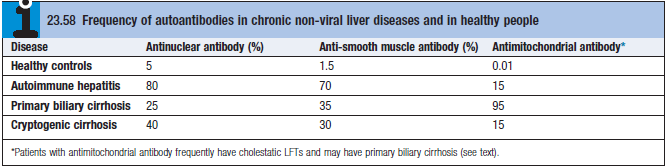
- Serological tests for autoAbs (See table)
- ANA – also occurs in connective tissue diseases and other autoimmune diseases
- Anti-SMA – also in infectious mononucleosis and other malignant diseases
- Elevated IgG levels – help diagnosis
- Liver biopsy – interface hepatitis with/without cirrhosis
- Hypersplenism – pancytopenia
Management
- Prednisolone [40mg/d PO]. Gradually tapered as pt and LFTs improve
- Maintenance therapy started once LFTs and IgG are normal
- Reduced dose prednisolone [ 5-10mg/d] (budesonide has lower side effects)
- Azathioprine [1-1.5mg/kg/d] – steroid sparring.
