Still’s disease
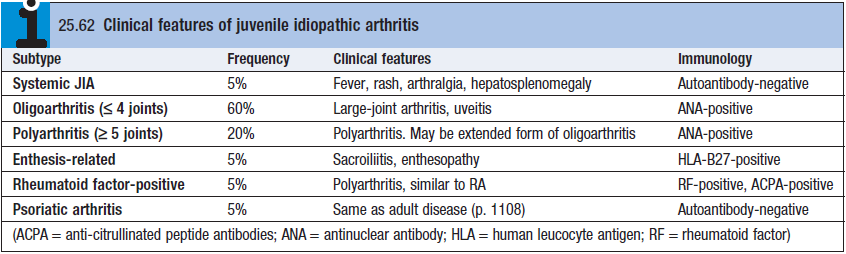
- 10% of all JRA cases. Under 5y. Male and Female equal.
- CF – Fever, maculopapular rash, arthritis, arthralgia, axis deviation, hepatosplenomegaly, pleurisy, pericarditis
- DDx – leukemia, neuroblastoma, infection
- Diagnosis – neurophilia, thrombocytosis, no auto-antibodies (seronegative),
Oligoarthritis (persistent)
- Most common 50% cases. <4 joint, knees/ankle/wrists, asymmetrical
- 3y, female,
- Uveitis (ANA +) – need to screen as blindness can occur.
- Extended form – more joints, usually destructive, after 6M of onset.
Polyarthritis (RF/ACPA +)
- Females, >8y, systemic disease, destructive, aggressive Tx
- Systemic disease, first small joints then large
Polyarthritis (RF/ACPA -)
- More common, 12y, females, risk of uveitis (if ANA +)
- Asymmetrical distro, cervical spine, TMJ, elbow
Enthesitis
- Teens, Male, asymmetric limb arthritis w/ enthesitis
- HLA-B27, iritis, childhood equivalent of ankylosing spondylitis but spine involvement rare
- HLA B27 –
- PAIR– psoriasis, ankylosing, IBD, reactive arthritis
Tx
- Early and aggressive – allows normal growth, remission is goal
- Systematic disease – IV pulsed methylprednisolone + methotrexate [10-15mg], use cytokine modulators if methotrexate fails. Etanercept and adalimumab commonly used.