Epidemiology/etiology
- Most common cause of death from malignancy in men and women
- Cigarette smoking accounts for >90% of cases
- Environmental – radon, asbestos, ionizing radiation
- Host factors – pulmonary fibrosis, HIV, genetics
Classification
Small cell carcinoma (SCC)
- Rapid growth
- Increased likelihood of metastases
- More responsive to chemotherapy and radiotherapy
- Arise from neuroendocrine (APUD) cells and secrete hormones
Non-small cell carcinoma (NSCC)
- Tend to be diagnosed in a localised form
- Divided into 3 histological types
- Adenocarcinoma – most common type
- Peripheral lesions
- Tend to invade the pleura
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Central lesions – originate centrally and grow outwards toward the bronchus
- Arise from epithelial cells, associates with production of keratin
- Large cell carcinoma
- Adenocarcinoma – most common type
Clinical features
- Cough >3 weeks – due to endobronchial erosion and irritation
- Breathlessness – due to airway occlusion
- Haemoptysis
- Chest pain – when tumour invades pleura
- Wheeze
- Hoarseness – compression of recurrent laryngeal nerve
- Nerve compression – due to pancoast tumour in lung apex
- Tumour invades the brachial plexus – causes C8/T1 palsy, muscle wasting and hand weakness
- Recurrent infections
Non-metastatic extrapulmonary manifestations
- Metabolic – weight loss, anorexia
- Endocrine (SCC) – SIADH, gynaecomastia
- Neurological – motor neuron disease, peripheral neuropathy
- Vascular – anemia, DIC
- Skeletal – clubbing
Metastatic spread
- Spreads to mediastinal, cervical, axillary lymph nodes
- Liver – anorexia, weight loss, nausea, right upper quadrant pain
- Adrenal glands
- Bone – pathological fractures
- Brain – space occupying lesions with mass effect, ↑ICP, headache
- Malignant pleural effusion
Investigations
- CT – shows extent of disease
- Include imaging of liver and adrenals
- PET scan – to show mediastinal lymph node involvement and distant metastasis
- Bronchoscopy – obtain biopsy
- If carcinoma involves the first 2cm of either main bronchus then the tumour is inoperable
- Percutaneous aspiration and biopsy
- Endobronchial ultrasound
- Others – FBC, LFTs
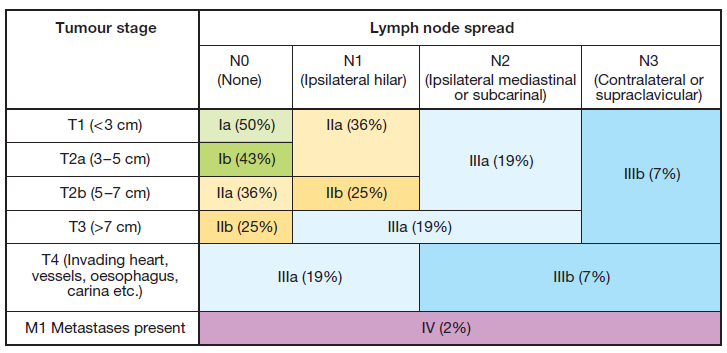
Staging – TNM
- Used for non-small cell carcinoma (not as prognostically useful for small cell carcinoma)
Treatment
- Surgical procedures – pneumonectomy, lobectomy, segmentectomy
NSCC
- Stage I – lobectomy
- Stage II – resection of primary tumour, en bloc resection of the hilar and lobar lymph nodes and mediastinal lymph node dissection
- Stage III – generally considered inoperable
- Adjuvant therapy
- Chemotherapy – cisplatin, pemetrexed
- CHART – continuous hyperfractionated accelerated radiotherapy
SCC
- Early stage is managed with chemotherapy – cisplatin and etoposide
