- Multisystem chronic granulomatous disorder
- Presents with bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy (LAD), pulmonary infiltration, skin/eye lesions,
Epidemiology/etiology
- Unknown etiology
- MC in North Europe
- F > M
- Possible etiological factors – atypical mycobacterium, occupational, EBV
 Clinical features
Clinical features
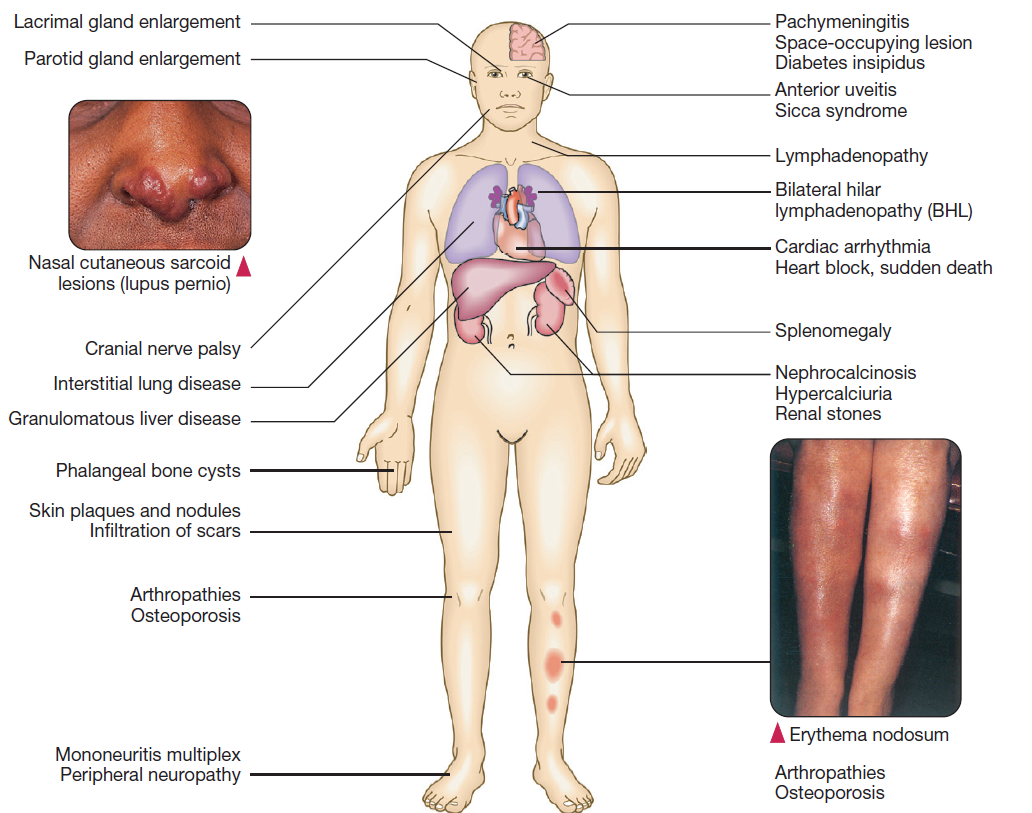
- Can involve any organs
- Lofgren’s syndrome – MC in young women
- Erythema nodosum, arthropathy, uveitis, bilateral hilar LAD, lethargy, fever
- Pulmonary symptoms – cough, dyspnoea, radiographic infiltrates, fibrosis
- Systemic involvement – see diagram
Diagnosis
- Lymphopenia
- Hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria
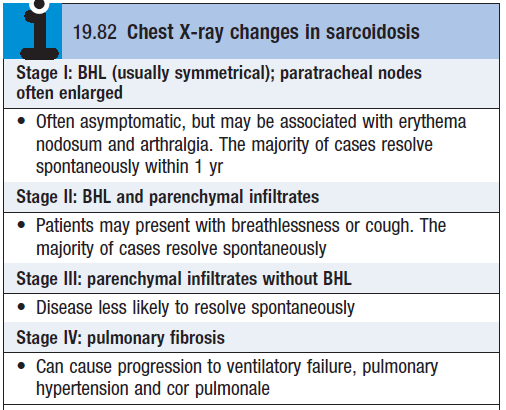
- CXR – to stage disease (see box), if non symmetrical consider tuberculosis
- Bronchoscopy – cobblestone mucosa
- Biopsy – non-caseating granulomas
- Bronchial alveolar lavage fluid – ↑CD4:CD8
Treatment
- NSAIDs
- Severe disease
- Prednisolone – If there is hypercalcemia, pulmonary/renal impairment, uveitis
- Methotrexate, azathoprine
- Cutaneous sarcoidosis with limited pulmonary involvement
 Chloroquine, thalidomide
Chloroquine, thalidomide
- Lung transplant
